Wanting to map out a whole project, forest, or mountainous area is usually a challenge from the ground. Even if you had the newest equipment with an experienced team, data collection would still take weeks or months to actually have mapped what’s required.
Even so, there are lots of facets that may happen to be missed. To stop repeat field site visits airborne LiDAR might be a choice. Airborne LiDAR systems combine a scanning laser, GPS, as well as an inertial measurement unit.
Laser pulses are directed for the ground usually with a moveable reflecting surface, which orients the consumer pulses in a scanning swath pattern. Processing and integrating ground based and airborne GPS data with inertial and laser range data makes a 3D data set referred to as a LiDAR Point Cloud. The resulting detailed data yields lots of benefits for businesses and organizations.
Applications areas are for projects where detailed accurate terrain details are required to make critical informed decisions. LiDAR offers the ways to see the bare earth ground surface aiding planning and operation decisions.
Spatial analysis is really as diverse because the user’s skill and imagination. This provides the consumer to be able to conduct analysis together with the entire project perspective in your mind. LiDAR applications can be broken into wide area and corridor mapping projects.
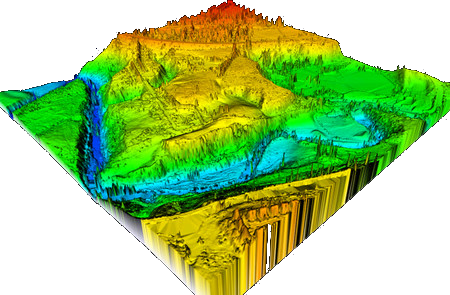
Wide area projects include topological mapping, flood plane modeling, urban area GIS, exploration area modeling, resource management, agricultural monitoring, and infrastructure modeling.
Corridor projects can vary from transportation mapping, pipeline route mapping, estuary environmental modeling, and transmission line thermal rating to name a few.
For example LiDAR for road design allows various best route scenarios being run in road engineering software to choose optimal road alignment. Road design parameters are accurately used in the field.
An accurate centre line determination and the way of cuts and fills can be established. Other benefits are the best stream crossing locations making use of their profiles and accurate grade determinations.
For the mining company a primary ground subsidence pilot project become once a year LiDAR survey. LiDAR accuracy and repeatability allowed a comparison of year over year to model subsidence and compute the total number of tailings.
LiDAR helps to yield important mission-critical data for users. Using LiDAR can be a cost-effective and timely approach to survey a region for geographical knowledge. As opposed to using manpower, money, and other resources, a LiDAR survey can map more detailed areas of the terrain in comparison with other remote sensing tools.
There is an capacity to view every nook and cranny in the terrain through the use of LiDAR technology. Think of the time and resources saved and also the many discoveries that await the next project.
More info about LIDAR vs RADAR web page: click.
